Internal and External Bisector of an Angle
Internal and External Bisector of an Angle: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Angle Bisector Theorem & Converse of Internal Angle Bisector Theorem etc.
Important Questions on Internal and External Bisector of an Angle

In , is the bisector of that intersects BC in D. If and then find BD : DC?
In the adjoining figure if exterior , then is equal to:

In the figure, Point is on the side of such that and . Ray is the bisector of of . If is ,then find .

In what ratio of line divides the line segment joining and ?
In the given fig. and is the bisector of . If and , then the value of will be
In the given figure, is the bisector of . If and . Find .
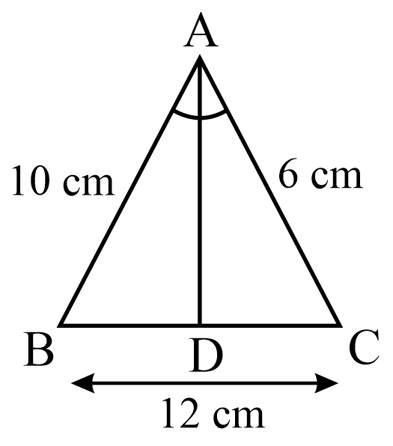
In , and. If bisector of meets at . Then is
and are the points on sides and , respectively of and intersect each other at T. If and , then

In the figure above, and . Find .

In the figure above, and . Find .

In the figure above, and . Find .
In the given figure, is the centroid of and point I is the intersection point of its three angle bisectors. and are given. Find the length of

In the given figure, G is the centroid of and If What is the length of the
In the given figure, is the centroid of and Find the length of

Find the value of by using the information given in figure.

In the given figure, and If what is the length of the
In the figure, is the centroid If and find the length of

In an equilateral triangle of side .
Then the area of triangle of is
From the diagram find the area of the
In area of region (in sq. units) are mentioned in the figure. Find the area of the quadrilateral .